Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous industries, from healthcare and finance to automotive and entertainment, by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making capabilities. He Magazine has covered multiple subjects regarding AI, yet AI is not just a technological advancement but a significant cost-saving opportunity in the boating industry. Integrating AI into boating systems brings many benefits, including optimized route planning, real-time obstacle detection, autonomous navigation, and predictive maintenance. These advancements enhance safety and efficiency and can lead to substantial reductions in operational costs and environmental impact. By leveraging AI, the boating industry can offer smarter, safer, and more sustainable solutions, making it a vital technological evolution in maritime operations.
Enhanced boat navigation systems are at the forefront of AI’s transformative impact on the boating industry. AI algorithms optimize route planning by analyzing vast amounts of data to determine the most efficient and safest paths. These systems can adjust real-time routes based on changing weather and sea conditions, ensuring optimal navigation and safety. For instance, advanced AI-powered navigation tools can reroute vessels to avoid storms or heavy traffic areas, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. Kongsberg Maritime, a leading provider of advanced technology, has developed an AI-based navigation system that integrates data from multiple sources, including weather forecasts and maritime traffic, to optimize ships' route planning. This system helps vessels navigate more efficiently and safely by continuously adjusting routes based on real-time conditions.
Obstacle detection has also seen remarkable improvements with AI technologies such as LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and computer vision. These systems can identify and track objects in the water, from other vessels to floating debris, providing real-time alerts to prevent collisions. Practical applications of these technologies are evident in various commercial and recreational boats, enhancing situational awareness and safety. Sea Machines Robotics, a company specializing in autonomous marine technology, including autonomous control systems and perception software for commercial vessels, has developed an advanced perception and navigation system that uses AI for obstacle detection and avoidance. This system employs cameras and LIDAR to detect objects in the water and automatically adjust the vessel's course to avoid collisions. It is used in various commercial vessels, including tugs and survey ships.
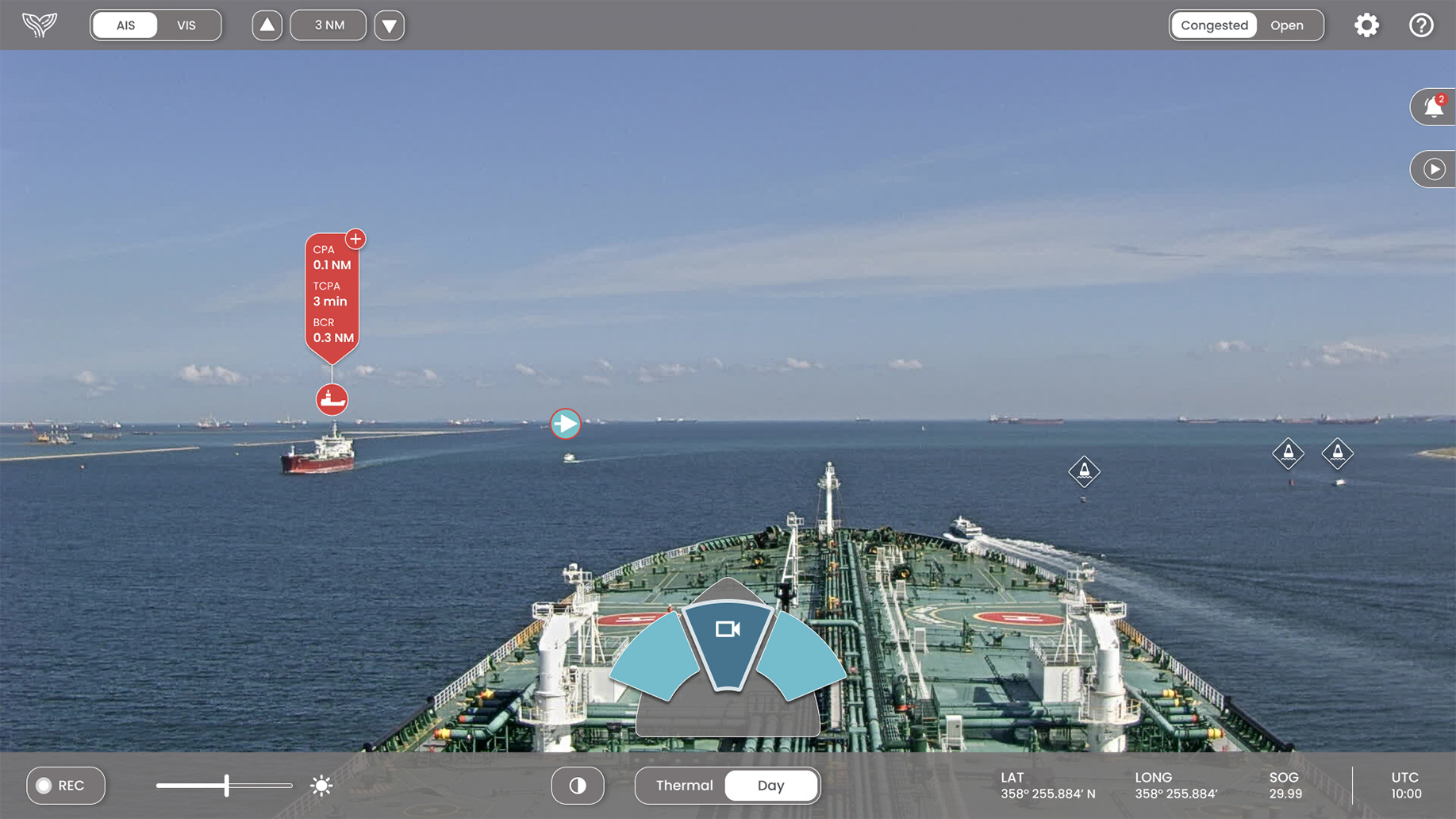
AI’s role in autonomous navigation is perhaps the most groundbreaking. Autonomous boats use AI to make decisions and operate without human intervention, relying on sensors and machine learning algorithms to navigate and perform complex maneuvers. Examples of autonomous boats include unmanned surface vessels (USVs) used for oceanographic research and commercial shipping, showcasing the potential of AI to revolutionize maritime operations by increasing efficiency, reducing human error, and expanding operational capabilities. Mayflower Autonomous Ship (MAS). This project, led by IBM and marine research organization Promare, resulted in the development of an autonomous ship to navigate the Atlantic Ocean without human intervention. The MAS uses AI for route planning, obstacle detection, and navigation, demonstrating the potential for AI-driven vessels to operate independently over long distances and in complex marine environments.
AI’s potential in predictive maintenance is revolutionizing how boats are monitored and maintained. Using sensors and advanced data collection methods, AI systems can continuously monitor various aspects of boat health, such as engine performance, hull integrity, and onboard systems. AI analyzes this data to detect anomalies and predict potential issues before they become critical. Machine learning models are at the core of this process, using historical and real-time data to foresee equipment failures, thus allowing timely interventions. For instance, Rolls-Royce has implemented predictive maintenance systems in their marine engines, successfully reducing unexpected breakdowns and improving operational efficiency. Caterpillar Marine employs predictive maintenance technology in their engines and power systems. Using machine learning models, they can predict failures with high accuracy, allowing for preemptive maintenance actions and reducing downtime and repair costs. Furthermore, AI schedules maintenance tasks to prevent downtime and extend the lifespan of boat components by optimizing maintenance schedules based on predictive insights. Siemens has developed an AI-driven predictive maintenance system for their marine solutions. This system schedules maintenance activities based on the analysis of operational data, which helps prevent unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of components, ensuring vessels remain operational and safe. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected repairs and associated costs and enhances vessels' safety and reliability, offering significant benefits for boat owners and operators.
Rolls-Royce, Sea Machines Robotics, and Siemens are among the frontrunners in integrating AI into boating technologies, demonstrating impressive progress and tangible benefits. For instance, Rolls-Royce's AI-driven marine engine monitoring system has significantly reduced unexpected breakdowns and improved operational efficiency. Sea Machines Robotics has also made significant strides with its advanced perception and navigation systems, which are now successfully used in commercial vessels like tugs and survey ships, offering superior obstacle detection and autonomous navigation capabilities. Siemens is another key player, using AI-driven predictive maintenance systems to optimize maintenance schedules, thereby preventing failures and extending the lifespan of marine components. These real-world applications vividly illustrate the substantial benefits of AI in boating, such as enhanced safety, reduced operational costs, and increased efficiency, underscoring the transformative potential of AI-enhanced boating systems.

The future of AI in boating holds exciting prospects and emerging technologies poised to transform the industry further. Advances in machine learning and data analytics will enable even more sophisticated predictive maintenance, ensuring boats operate at peak efficiency and reliability. Enhanced autonomous navigation systems will incorporate more advanced AI algorithms, improving the ability to handle complex marine environments and making fully autonomous vessels more prevalent. Innovations in sensor technology and IoT integration will provide richer data for AI systems, enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities. AI-driven energy management systems will also optimize fuel consumption and integrate with renewable energy sources, contributing to significantly more sustainable maritime operations. As these technologies evolve, the boating industry will witness significant improvements in safety, efficiency, and environmental impact, heralding a new era of intelligent, autonomous, and eco-friendly marine operations.
Implementing AI in boating presents various technical and ethical challenges that demand careful consideration. From a technical perspective, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of AI systems in dynamic marine environments is a significant challenge. Data quality, sensor reliability, and algorithm robustness must be addressed to achieve safe and effective AI-driven operations. Moreover, ethical considerations regarding the use of AI in decision-making processes, particularly in autonomous navigation, raise important questions about accountability and liability in the event of accidents or incidents. Safety, security, and privacy are paramount when integrating AI into boating systems. Safety protocols and fail-safe mechanisms must be rigorously implemented to prevent accidents and protect passengers, crew, and marine assets. Cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguard AI systems from malicious attacks that could compromise navigation, communication, or control systems. Additionally, privacy concerns arise from the collection and analysis of data by AI systems, necessitating transparent policies and practices for data handling and usage to protect individuals' rights and information. Balancing technological advancement with these challenges and considerations is crucial for AI's responsible and successful integration in the boating industry.
In conclusion, integrating AI in boating offers the maritime industry many benefits and transformative potential. AI-powered navigation systems enhance safety and efficiency through optimized route planning, real-time obstacle detection, and autonomous navigation capabilities. Predictive maintenance driven by AI ensures proactive management of boat health, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of critical components. These advancements improve operational performance and contribute to cost savings and environmental sustainability. Looking ahead, the future of AI in the maritime industry holds immense promise. Emerging technologies and trends such as advanced machine learning algorithms, IoT integration, and energy management systems will further enhance AI's capabilities in boating. As AI continues to evolve, we expect to see increased automated intelligent decision-making processes and improved safety measures across the maritime sector. However, alongside these advancements, it's crucial to address the technical, ethical, and regulatory challenges associated with AI implementation in boating. Safety, security, and privacy considerations must remain at the forefront of development efforts to ensure AI's responsible and beneficial integration in the maritime industry. Overall, AI has the potential to revolutionize boating operations, making them safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly. By harnessing the power of AI technologies responsibly, the maritime industry can navigate towards a more sustainable and prosperous future.














